Anthropic urges AI regulation to avoid catastrophes
In an era where artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving, the conversation surrounding its regulation has never been more pressing. As breakthroughs in AI technology promise to revolutionize industries and reshape our daily lives, a growing chorus of experts and organizations is sounding the alarm over the potential risks associated with unchecked development. Among them is Anthropic, a prominent player in the AI landscape, which has recently taken a definitive stance on the need for comprehensive regulatory frameworks. Urging policymakers to act decisively, Anthropic warns of the catastrophic consequences that could arise if innovation continues without adequate oversight. This article delves into the implications of their call for regulation, exploring the balance between fostering technological advancement and ensuring the safety and ethical integrity of AI systems.
The Imperative of Responsible AI Development
As the landscape of artificial intelligence evolves, the push for responsible AI development becomes more crucial than ever. Organizations are urged to establish rigorous frameworks that integrate ethical considerations into the AI lifecycle, ensuring alignment with both societal values and regulatory standards. Key strategies include:
- Governance Frameworks: Implementing structured governance mechanisms to oversee AI operations.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging teamwork across departments to address the multifaceted challenges of AI.
- Human-Centric Design: Prioritizing user safety and ethical implications from the outset of AI development.
Moreover, leveraging a three lines of defence model can facilitate proactive risk management. This approach encompasses:
| Line of Defence | Role |
|---|---|
| 1st Line | Operational management controls daily AI risks. |
| 2nd Line | Specialized teams oversee compliance and risk management. |
| 3rd Line | Internal audit provides independent assurance on risk management. |
By embedding these principles into their AI strategies, organizations can better navigate the complexities of AI technology while mitigating potential risks of catastrophic outcomes.
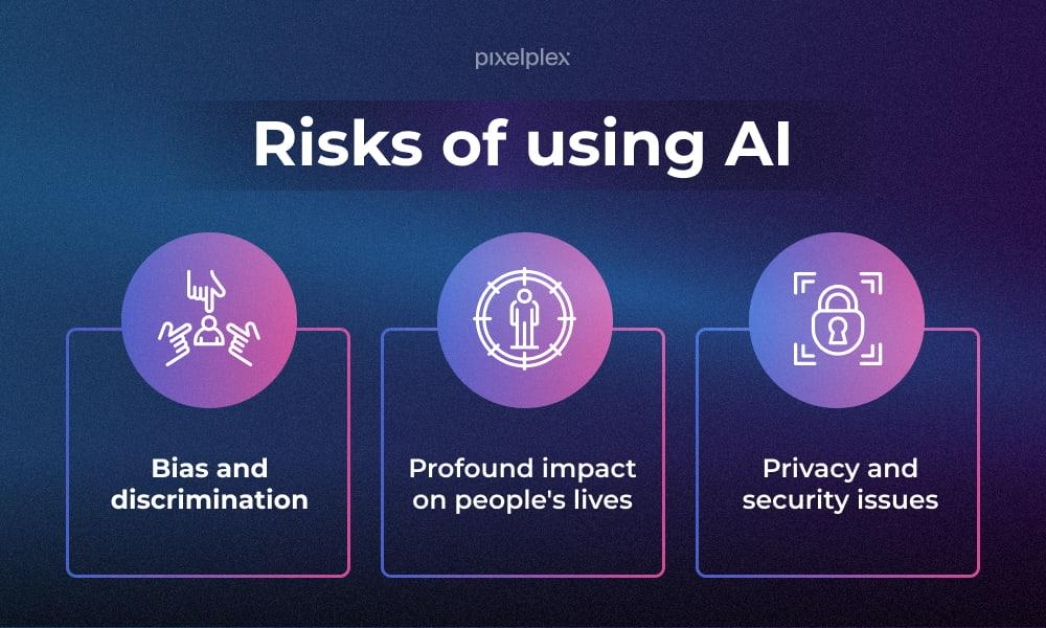
Assessing the Risks of Unregulated AI Technologies
As AI technologies proliferate without sufficient oversight, the potential for devastating consequences rises dramatically. Unregulated AI may lead to a myriad of risks, affecting various facets of society, including:
- Ethical Concerns: Algorithms could perpetuate biases or violate individual rights, leading to unfair treatment.
- Security Threats: Malicious actors could exploit AI systems for cyber attacks, endangering both individuals and organizations.
- Environmental Impact: Unchecked development may result in unsustainable practices that harm ecosystems.
It is critical to preemptively address these dangers through comprehensive regulations that establish clear boundaries for AI research and deployment. Below is a simple comparison of potential regulatory approaches:
| Regulatory Approach | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Regulation | Flexibility for innovation | Lack of accountability |
| Industry Standards | Encourages collaboration | Varied adoption rates |
| Government Regulation | Provides clear legal frameworks | Potential to stifle innovation |

Proposed Guidelines for Effective AI Governance
Establishing robust frameworks for AI governance is essential to mitigate risks and foster trust in AI technologies. Here are some proposed guidelines to shape effective governance:
- Data Governance: Ensure comprehensive oversight of data management, including origin, sensitivity, and lifecycle, to maintain the integrity and security of the data used in AI systems. Transparency in data sourcing can reduce risks associated with sensitive information [[1]]
- Inclusive Design Practices: Implement policies that promote diversity and inclusivity in AI system design, ensuring that all voices are heard in the development process. This fosters an equitable technological landscape [[2]]
- Accountability Mechanisms: Develop clear accountability structures to oversee AI deployments. Establishing roles and responsibilities can streamline accountability and ensure that stakeholders are answerable for AI outcomes [[3]]
- Continuous Monitoring: Incorporate ongoing assessments and audits of AI systems to evaluate their performance and ethical implications. Adopting a proactive stance can help identify potential biases and operational failures early on.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve a diverse range of stakeholders, including ethicists, technologists, and affected community members, in the decision-making process. This engagement can enhance the relevance and effectiveness of AI policies.
Building a Collaborative Framework for Global AI Regulation
In light of the accelerating advancements in artificial intelligence, it is crucial to forge an inclusive and comprehensive framework for global regulation that fosters collaboration among various stakeholders. This framework must encompass:
- International Collaboration: Encourage nations to engage in dialogue, sharing best practices and regulatory approaches to ensure that advancements in AI are controlled at a global level.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve a diverse array of stakeholders, including technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public, to craft regulations that reflect broad societal values and priorities.
- Transparency Measures: Develop protocols that mandate clear disclosures from AI developers about capabilities, limitations, and potential harms, facilitating informed conversations about risks and ethical considerations.
- Dynamic Regulatory Approaches: Adapt to the fast-paced changes in AI technology by implementing a regulatory framework that is flexible and responsive, capable of evolving alongside emerging innovations.
To illustrate the essential elements of this collaborative regulatory structure, consider the table below:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Principles | Establish foundational ethical guidelines for AI development. |
| Compliance | Set clear expectations and penalties for non-compliance with regulations. |
| Review Mechanisms | Implement continuous monitoring to assess AI systems’ impact on society. |
| Innovation Support | Encourage responsible innovation through funding and resources for AI research and development. |
Final Thoughts
As we stand at the crossroads of technological advancement and societal responsibility, Anthropic’s call for AI regulation serves as a potent reminder of the delicate balance between innovation and safety. The potential of artificial intelligence to reshape our world is both exhilarating and daunting, inviting us to ponder not only what is possible but what is prudent. By advocating for comprehensive guidelines and frameworks, Anthropic highlights the urgency of collaborative efforts among policymakers, experts, and industry leaders to steer AI development toward a future that prioritizes human welfare. The dialogue surrounding AI regulation is not merely about limitation; it is about harnessing technology in a way that safeguards against its inherent risks while empowering us to thrive. As we continue this conversation, let us be guided by foresight and caution, ensuring that we not only envision a brighter future but also actively work to realize it—one informed decision at a time.